Introduction to Machine Learning and its Applications
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning (ML) is a subfield of artificial intelligence that involves the development of algorithms, making the computer learn by studying data and statistics, and finally analyses data and learning to predict the outcome.
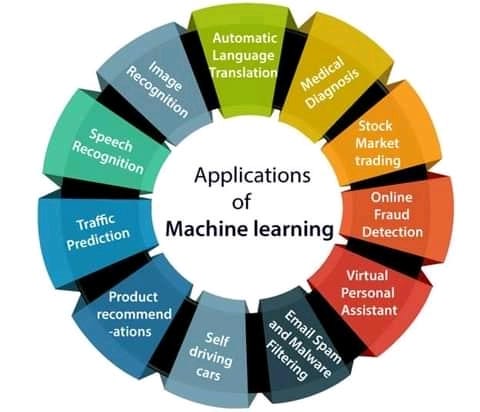
Difference between AI, ML, and Deep Learning
Artificial Intelligence:
AI means simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think like humans and mimic their actions.
Machine Learning
ML is making the computer learn by studying data and statistics.ML is the first step in the direction of AI, it involves analysing data and learning to predict the outcome.
Deep Learning
DL is a subset of Machine learning based on Artificial Neural Networks. it can be used to increase the complexity and improve the performance of the Machine Learning algorithm
Data Science covers (AI, ML and DL). is a study of data to extract meaningful insight for business
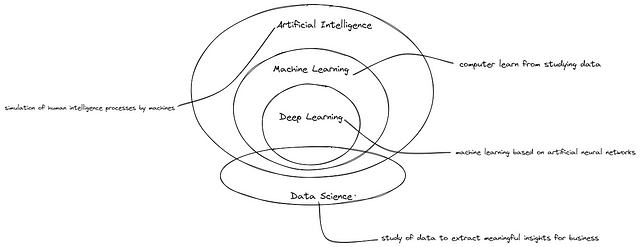
Application of Machine Learning
Machine learning is a powerful aspect that can be applied to a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of those applications include:
- Medical Diagnosis: Machine learning is now being widely used in medical diagnosis to help healthcare professionals make more accurate and timely decisions.
2. Image and video recognition: Machine learning algorithms can be used to identify and classify objects and patterns within images and videos.
3. Recommendation systems: Machine learning algorithms can be used to recommend items to the user, for example watching movies on YouTube, Netflix and Online shopping.
Others include Automatic language translation, online fraud detection, self-driving cars, stock market trading and traffic prediction.
Conclusion
Machine learning is rapidly growing in today’s world and has applications in various aspects, including healthcare, finance, and security. It has the ability to handle complex and large datasets.

Comments